Techniques for measuring oxygen, carbon dioxide and minute ventilation that were relatively quick, accurate and inexpensive to perform were developed in the late 1800’s. This made it possible to make a variety of measurements on lung physiology, including exercise.
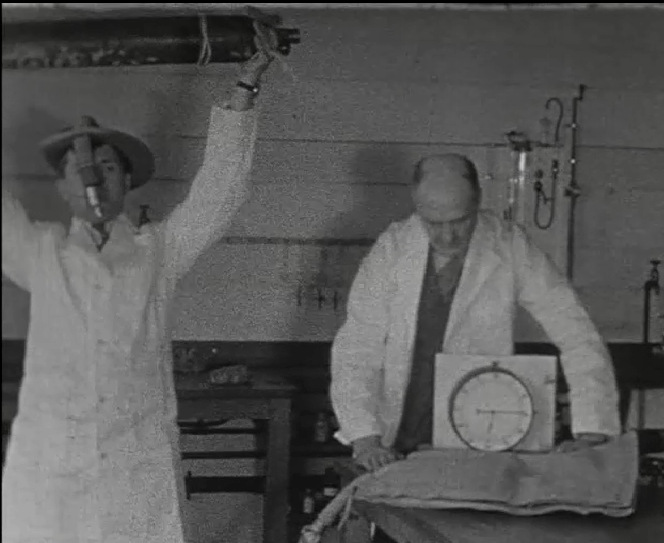
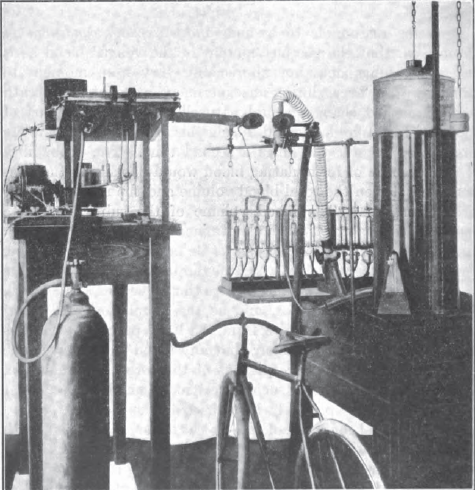
Exercise testing with spirometer, 1895. Found on Flickr. Image from page 180 of “Transactions – American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers” (1895)
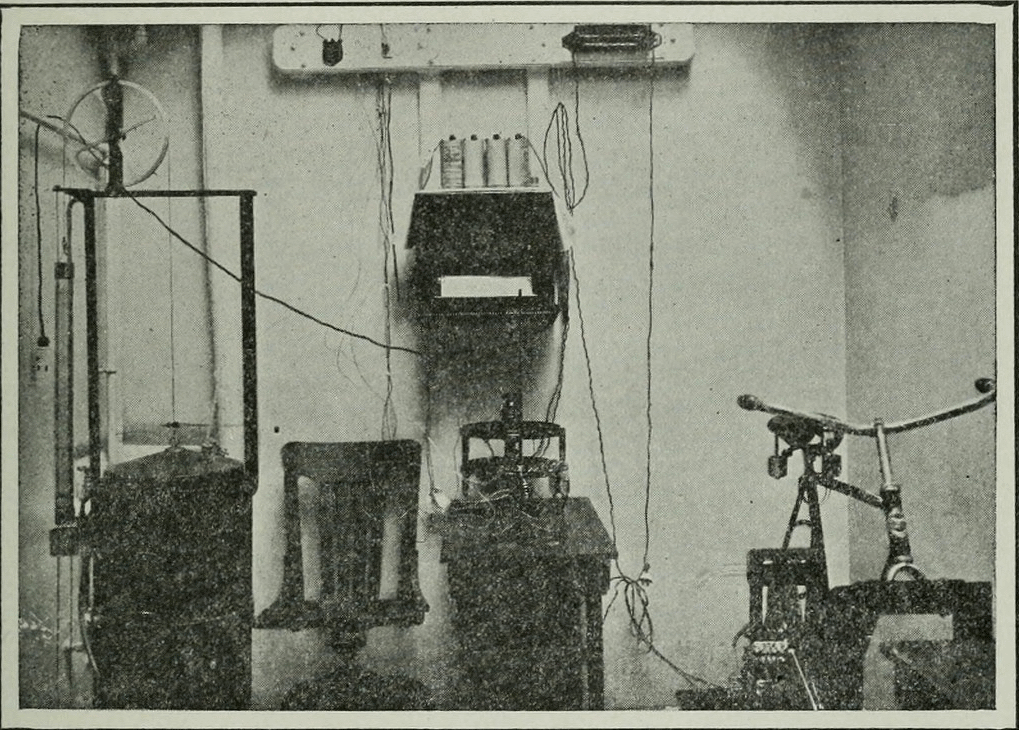
“Fig. 18 View in Observation Room looking toward south wall. In the upper center ofthe picture is the Body Temperature Recorder. In the lower right corner Is the Bicycle Ergometer, the controlling rheostat being located on the table. At the left is seen a spirometer used to collect and measure exhaled air.”
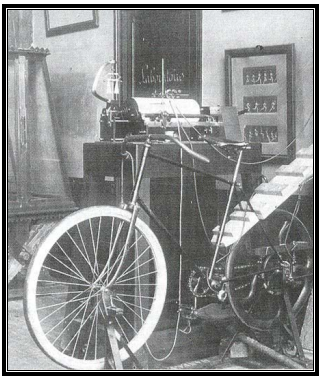
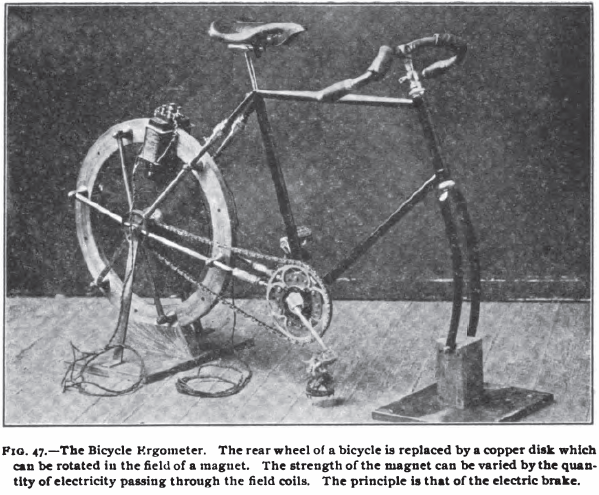
Bicycle Ergometer, 1896. First bicycle ergometer, developed in 1895 by Elisee Bouny, who worked for Jules-Etienne Marey. Photograph was dated 1896. From a 2003 PhD dissertation by Yaser Mahfouz Atwa Saad Elgohari.
Bicycle Ergometer, 1905. From A Respiration Calorimeter with Appliances for the Direct Determination Oxygen, By Wilbur Olin Atwater, Francis Gano Benedict. Published by Carnegie Institution of Washington, 1905, page 165.
Exercise testing in the field, 1908. From: Handbuch der Physiologischen Methodik, by Robert Tigerstedt, published by Verlag von S. Hirzel, Leipzig, 1908, page 32. Described as manufactured (assembled?) by Hanriot and Richet. It measured exhaled air volume but also had the ability to take samples of exhaled air for later gas analysis.
Exercise testing in the field, 1910. Intended for field studes of human ventilation. Included a gas sample tube (at right). From: Methodik des Energiestoffwechsels, by Von J. E. Johansson, Handbuch der biochemischen arbeitsmethoden, Volume 3, Part 2, Edited by Emil Abderhalden, published by Urban & Schwarzenberg , 1910, page 1157.
Bicycle ergometry, 1913. From Muscular Work: A Metabolic Study with Special Reference to the Efficiency of the Human Body as a Machine, Issue 187, By Francis Gano Benedict and Edward Provan Cathcart, published by Carnegie institution of Washington, 1913. Un-numbered front page.
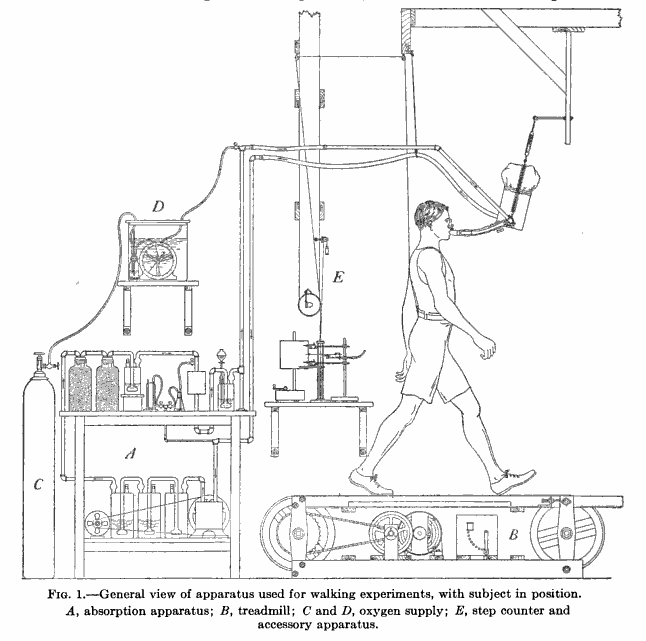
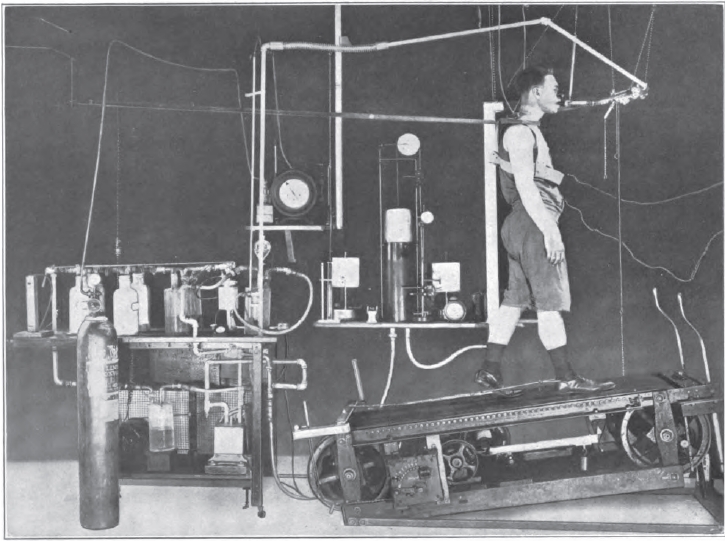
Exercise testing, 1915. From: Energy transformations during horizontal walking, Issue 231, by Frances Gano Benedict, page 32, published by Carnegie Institution of Washington, 1915.
Exercise testing, 1915. The spirometer was described in the text as a 30 liter recording spirometer. From: Boothby WM. The determination of the circulation rate in man at rest and in work. Amer J Physiol, 1915, v37, p383.
Bicycle Ergometer, circa 1915. Found on the Steno Museum Collection website. Described as “a black stationary bike without wheels but instead mounted on four obliquely positioned legs, standing in a black iron frame on the floor.” It appears to be electromagnetically braked and is attributed to a design of August Krogh. Manufactured by the Copenhagen Electric Motor Factory between 1910 and 1920.
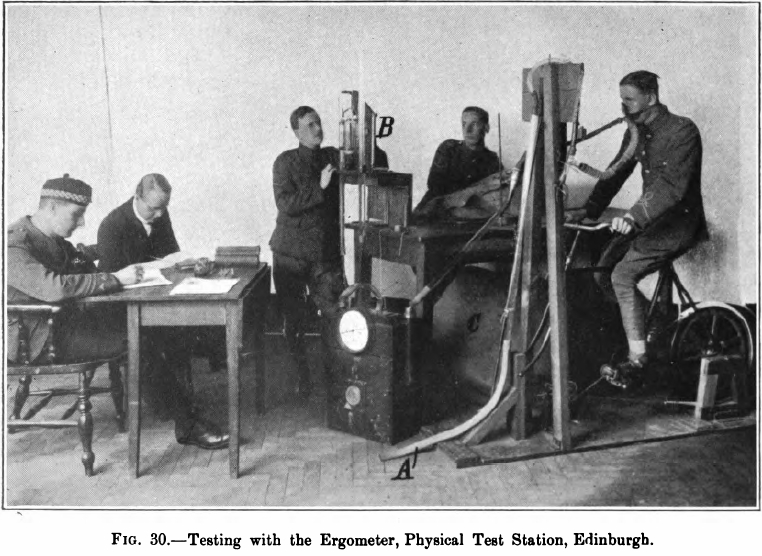

Exercise testing, 1920. From The Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, Advisory Council, Second Report of the Mine Rescue Apparatus Committee, Published by His Majesty’s Stationary Office, 1920, page 58.
Exercise testing, 1922. From: Gaseous Exchange and physiological requirements for level and grade walking, by Henry Monmouth Smith, 1922, Frontpiece.
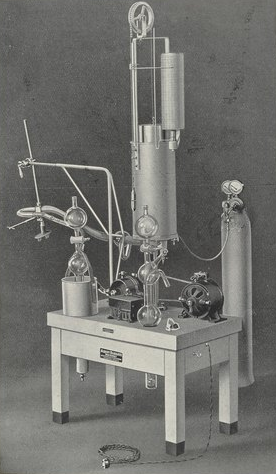
Knipping SpiroErgometry Apparatus, 1927. From “The gas metabolism apparatus according to Dr. Knipping. Its application and treatment.”, by Albert Dargatz, published 1927 in Hamberg, Germany.
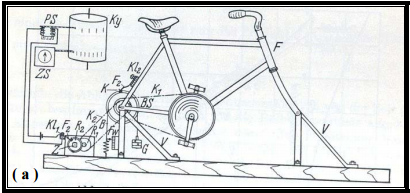
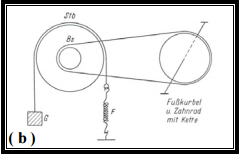
Bicycler Ergometer, 1935. Bicycle ergometer developed by Holzer and Kalinka in 1935. It used friction from a metal strap around the wheel. Varying weights attached to the strap were used to adjust the workload. From a 2003 PhD dissertation by Yaser Mahfouz Atwa Saad Elgohari.
Exercise testing, 1935. Found at Europeana.Eu. From an educational film entitled “Methods of measuring metabolism and basal metabolism Krogh and Douglas bag”, Produced by the Department of Physiology, Cambridge University, 1934. Using a Douglas bag to collect exhaled air during exercise.
Bicycle ergometry, 1950. From: Studien uber die Pathophysiologie der Atmung bei der Silikose Die Lungenfunktion im Arbeitsversuch by P.H. Rossier and A. Buhlmann, 1950, page 58.
Exercise testing, 1954. Pictured standing is Sepp Herberger, German football coach. Equipment manufacturer was not named but is likely Dargatz. From: page 40 of of a 2003 doctoral dissertion by Yaser Mahfouz Atwa Saad Elgohari.
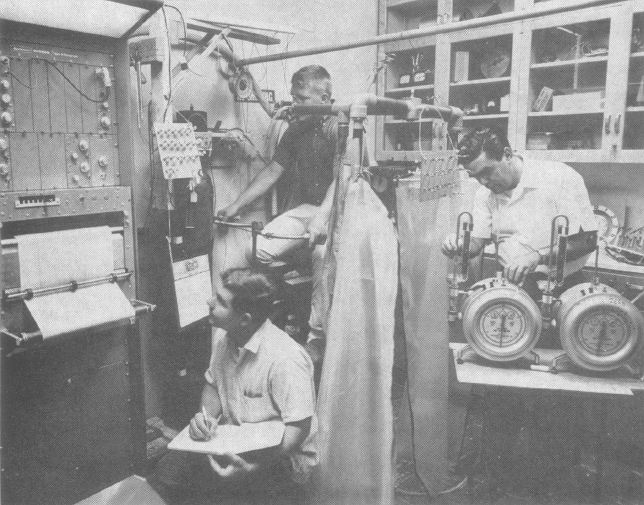
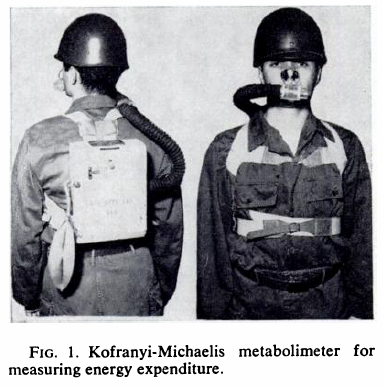
Exercise testing in the field, 1955. From Consalazio CF, Energy expenditure studies in military populations using Kofranyi-Michaelis respirometers, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, December 1971, page 1432.
“This simplified and compact unit is fairly small, 20 by 27 by 11 cm, weighs 3 kg, and consists of a dry gas meter for measuring the total volume and temperature of expired air. The aliquoting device can eb set to continuously remove 0.3 or 0.6% of each breath of expired air into a 500-ml butyl rubber bag. One important feature is that these aliquots can be taken over fairly long periods of time. These aliquots are analyzed for their CO2 and O2 concentration by conventional procedures and the eventual calculation of energy expenditure.”
Exercise testing in the field, 1956, using the Integrating Motor Pneumograph. From Popular Science, March 1956, page 256.
From New Scientist, November 29, 1956, page 21.
“…it will be necessary to measure their bodily energy exchanges; and this can be done with a modern apparatus called the IMP (integrating motor pneumotachograph). This consists of a light air pump and flowmeter housed in a plastic box, which connects on one side with a mask fitted over the face and on the other with a sample-collecting unit packed in a bag worn on the back. The IMP measures, over a given time, the total volume of air breathed out by its wearer, and from this expired air it automatically takes representative (or integrated) samples. The whole apparatus is so light, well-fitted and comfortable that it can be worn easily during violent exercise or peaceful sleep.
“The IMP was designed by Mr. H.S. Wolff, of the Human Physiology Division of the National Institute for Medical Research, to enable physiologists to study human energy exchanges under conditions ranging from swimming the Channel to bathing a baby. It has attachments allowing the wearer to drink through a tube or blow a whistle; though as yet the IMP cannot measure man’s energry exchanges while he is chatting, smoking, shaving or eating. It is manufactured by J. Langham Thompson.”
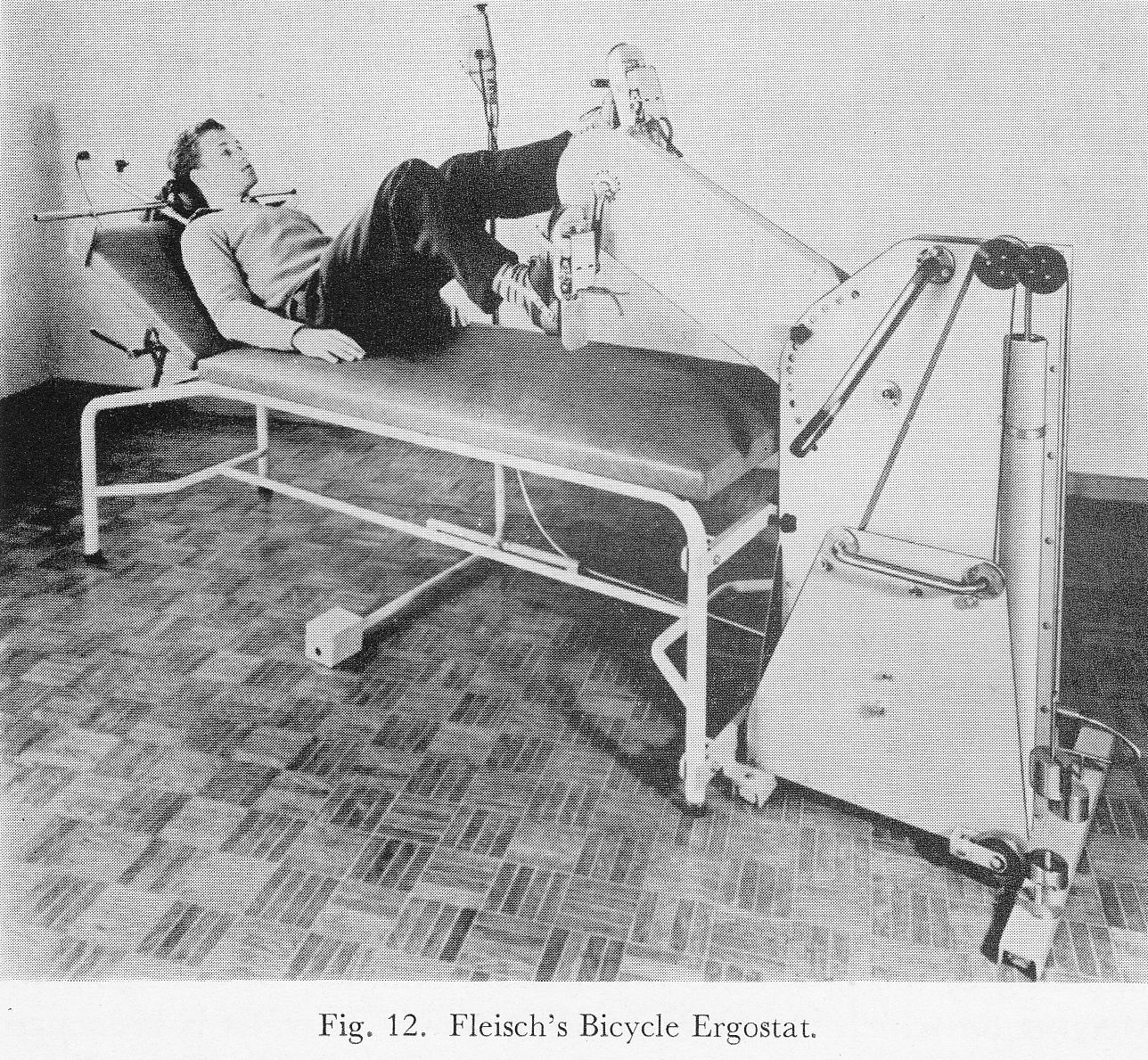
Bicycle Ergometer, 1960. From “New methods of studying gaseous exchange and pulmonary function” by Alfred Fleisch, published by Charles C. Thomas, 1960, page 51.
Exercise testing, 1963. Photo found at esport.dshs-koeln.de. Exercise testing using a hand-cranked electrically braked ergometer. Spirometer is described as closed-circuit Knipping Model 210 D, manufactured by Dargatz, a German company.
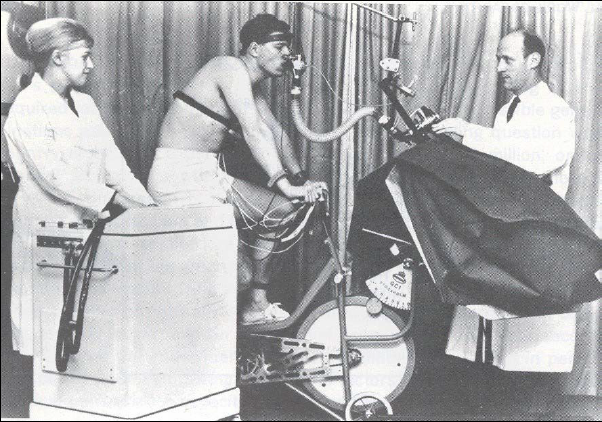
Exercise Testing, 1965. Tidal volume was monitored with a heated Fleisch pneumotachograph that was mounted downstream of a Hans Rudolph two-way high velocity valve. Exhaled air was collected in plastic and neoprene bags, the volume subsequently measured with precision gas meters. Gas concentrations were measured with a gas chromatograph. The bicycle eergometer used friction resistance to maintain and steady workload and the subject pedealed to a metronome. Taken from the “The inhalation of the photochemical smog compound peroxyacetyl nitrate” by Leon E. Smith EdD in AJPH volume 55, no 9, Sept 1965, page 1460.
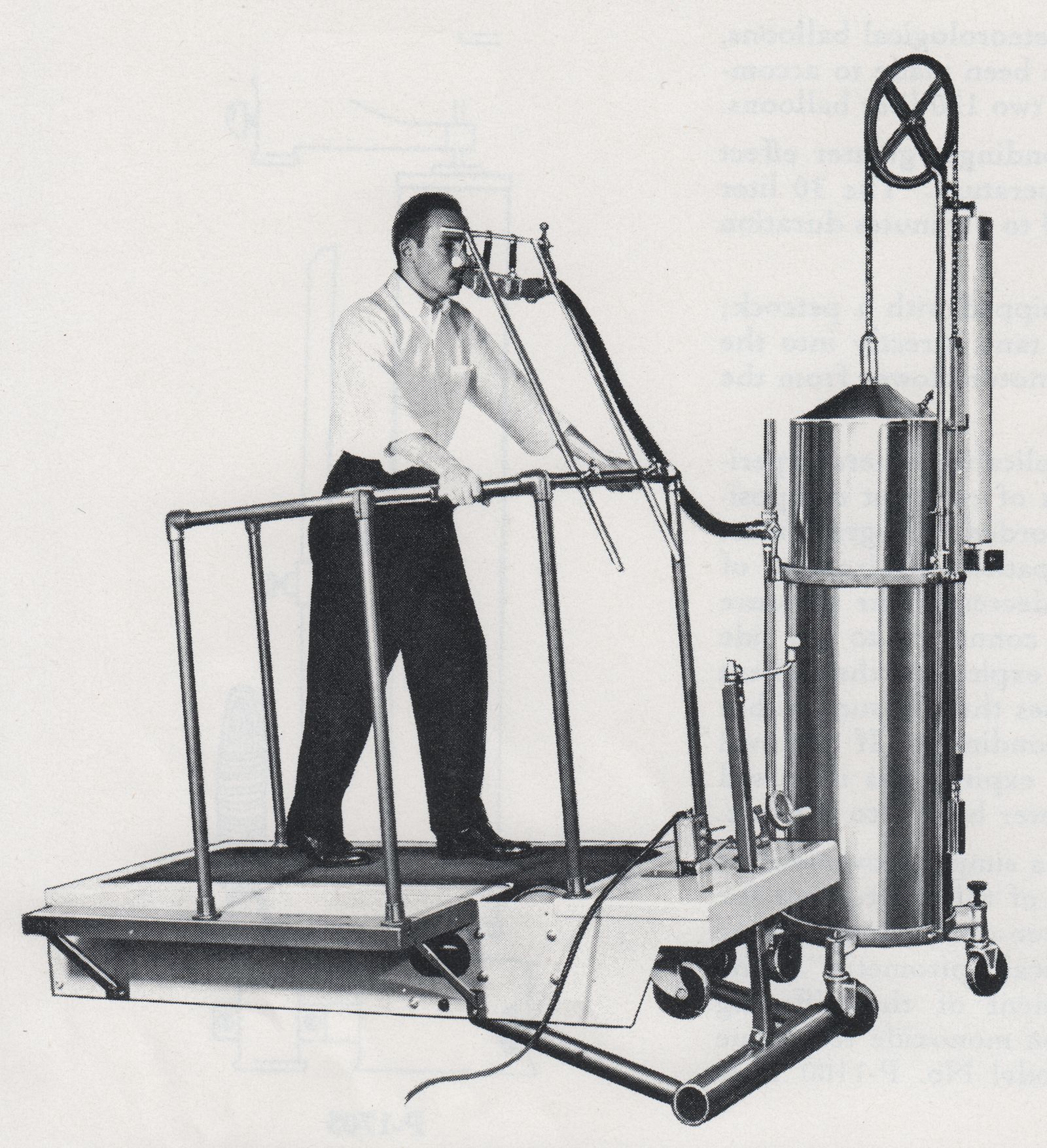

Exercise testing, 1966. Using a Collins treadmill and Tissot Spirometer. From ‘A Catalog of Pulmonary Function Equipment and Accessories’, W. E. Collins Inc., 1966, page 42.
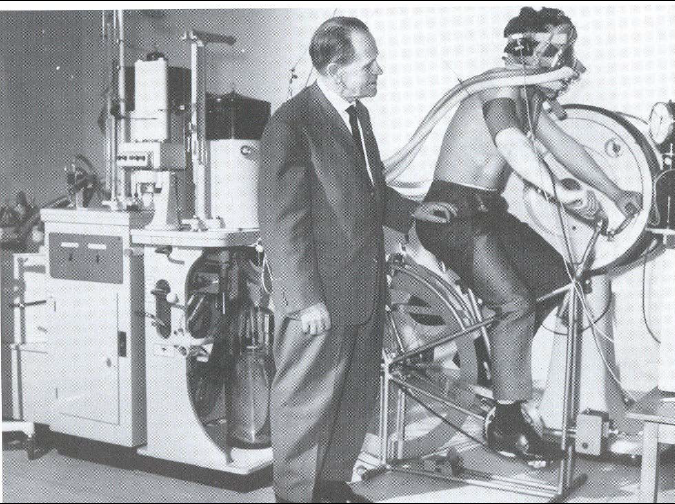
Exercise Testing, 1970. Using the Douglas bag in the measurement of oxygen uptake. Ergometer was a mechanically braked Åstrand-Ergometer. Photo taken at the Stockholm Sports Medicine Laboratory of the Swedish College of Physical Education. Professor Per-Olaf Åstrand, MD on the right. From: page 20 of of a 2003 doctoral dissertion by Yaser Mahfouz Atwa Saad Elgohari.

Exercise Testing, 1972. From “Laboratory manual for physiology of exercise”, by Laurence E. Morehours, Published by C.V. Mosby, 1972, page 107.
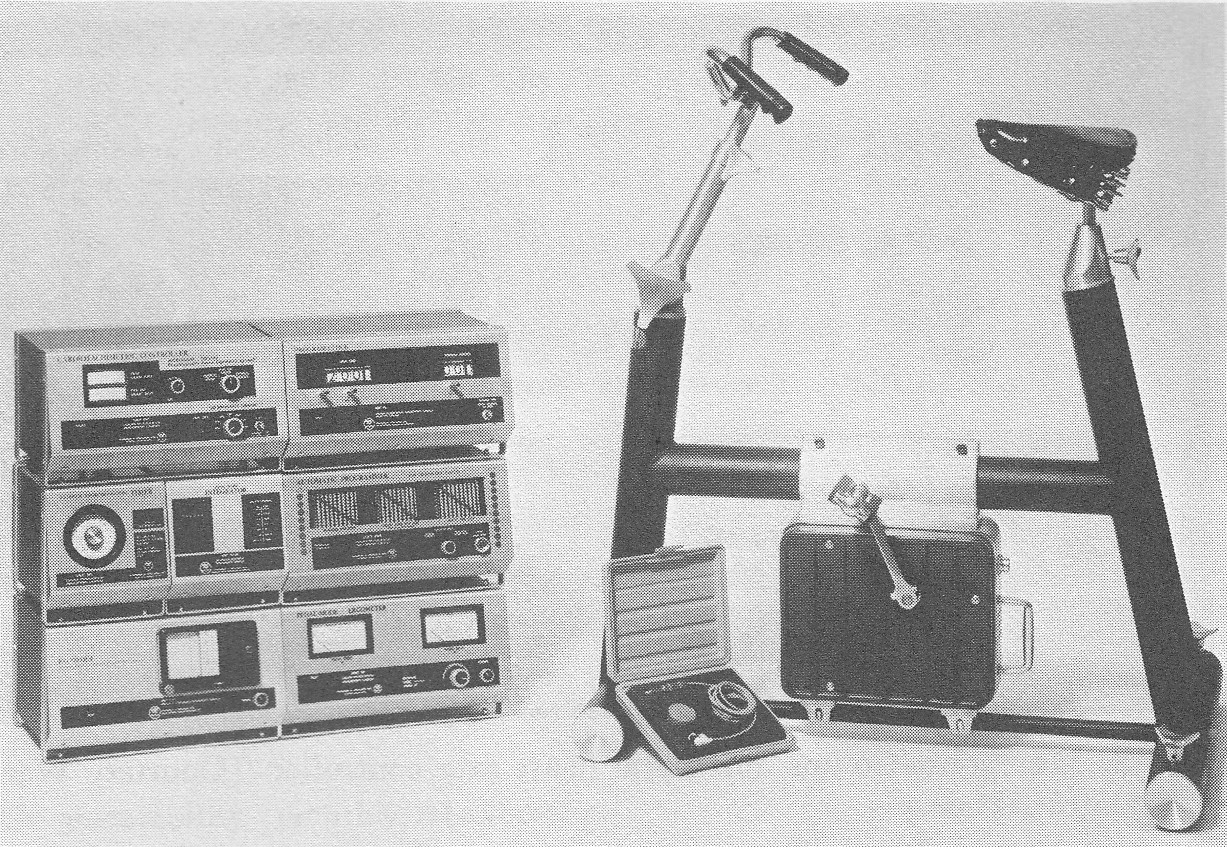

Collins Bicycle Ergometer, 1972. From “Laboratory manual for physiology of exercise”, by Laurence E. Morehours, Published by C.V. Mosby, 1972, page 127.
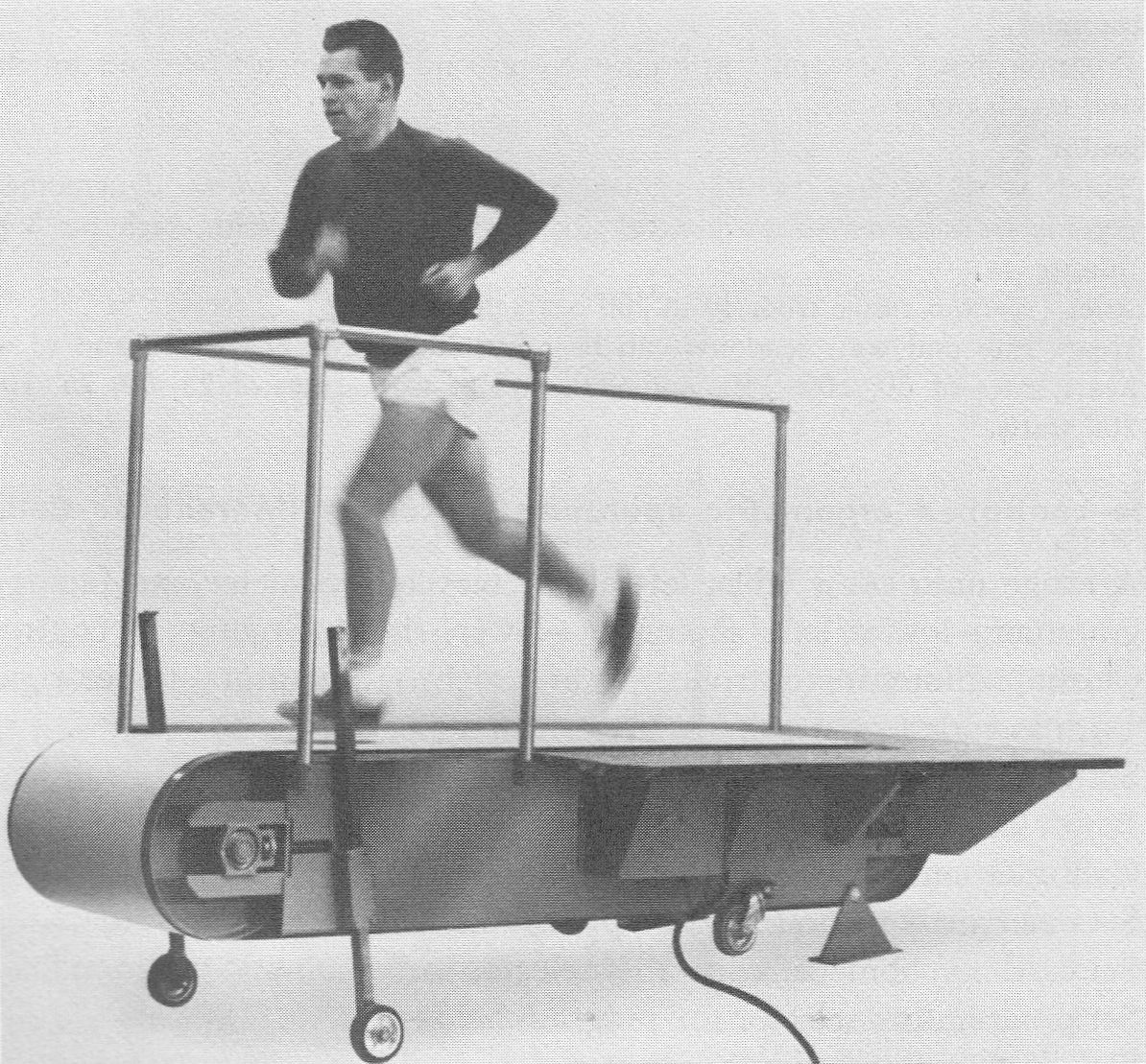

Quinton Treadmill, 1972. From “Laboratory manual for physiology of exercise”, by Laurence E. Morehours, Published by C.V. Mosby, 1972, page 130.
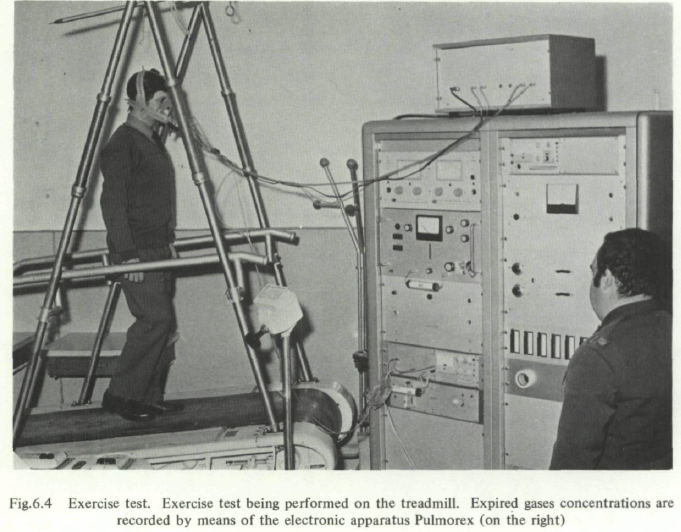
Exercise testing, 1974, Pulmorex. From: Survey of Current Cardiovascular and Respiratory Examination Methods in Medical Selection and Control of Aircrew by A. Scano, NATO Agardograph No. 196, published December 1974, page 76. The Pulmorex system was manufactured by Fenyves et Gut. Switzerland.
Exercise testing, 1974. From: Survey of Current Cardiovascular and Respiratory Examination Methods in Medical Selection and Control of Aircrew by A. Scano, NATO Agardograph No. 196, published December 1974, page 76.
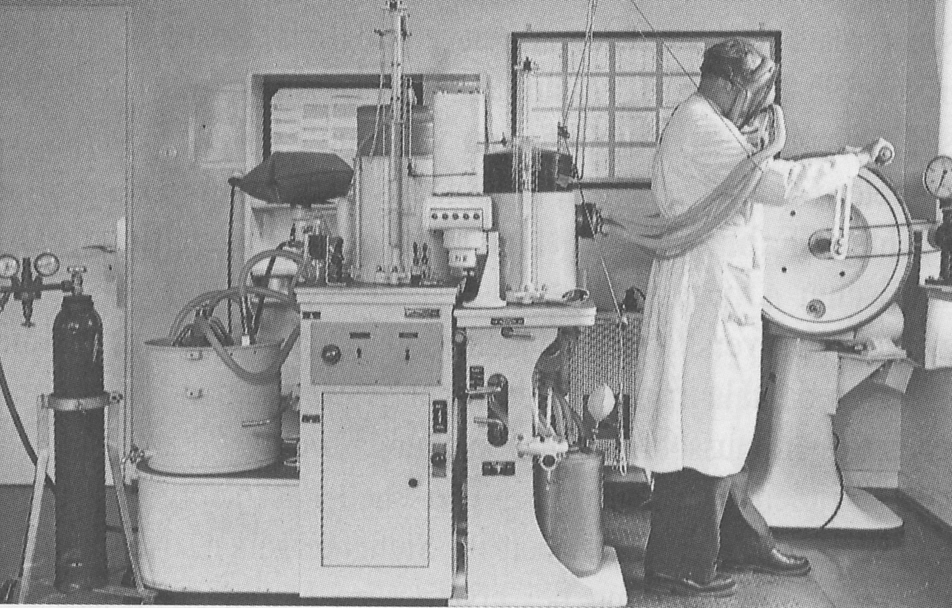
Exercise testing, 1974. From: Survey of Current Cardiovascular and Respiratory Examination Methods in Medical Selection and Control of Aircrew by A. Scano, NATO Agardograph No. 196, published December 1974, page 58. Test system is a Fleisch Metabograph.

Exercise testing, 1970’s, Godart. Image from Mr. Kevin Hogben International Sales and Product Specialist Manager for Medisoft
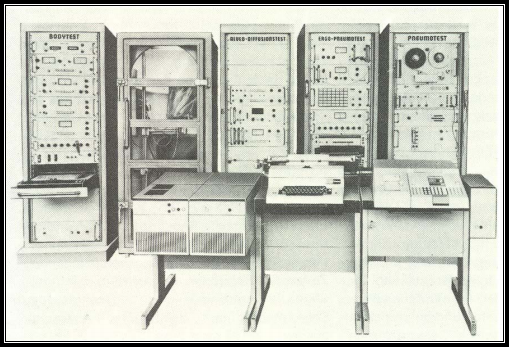
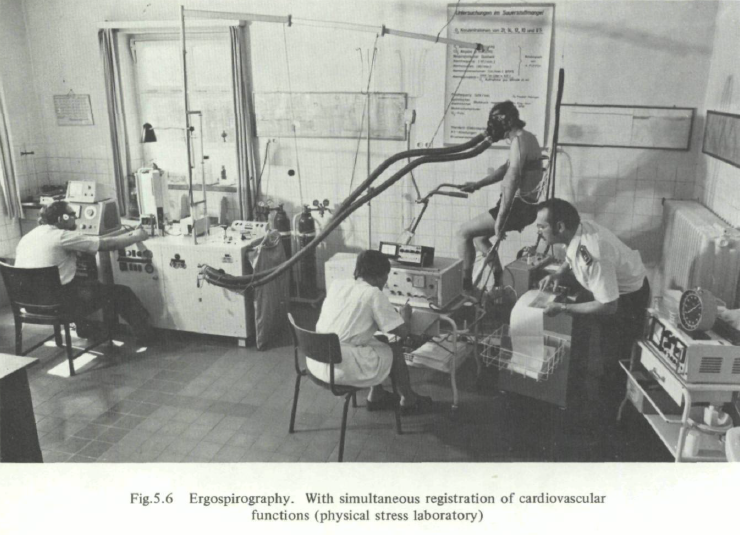
Computerized Exercise Testing System, Jaeger, 1974. Photo caption (translated from German) “Computerized complete measuring station for the cardiorespiratory system Functional Diagnostics by E. Jaeger, Würzburg, in the Spiroergometry Laboratory of the Department of Sports Medicine of JLU Giessen.”
From a 2003 PhD dissertation by Yaser Mahfouz Atwa Saad Elgohari, page 58.
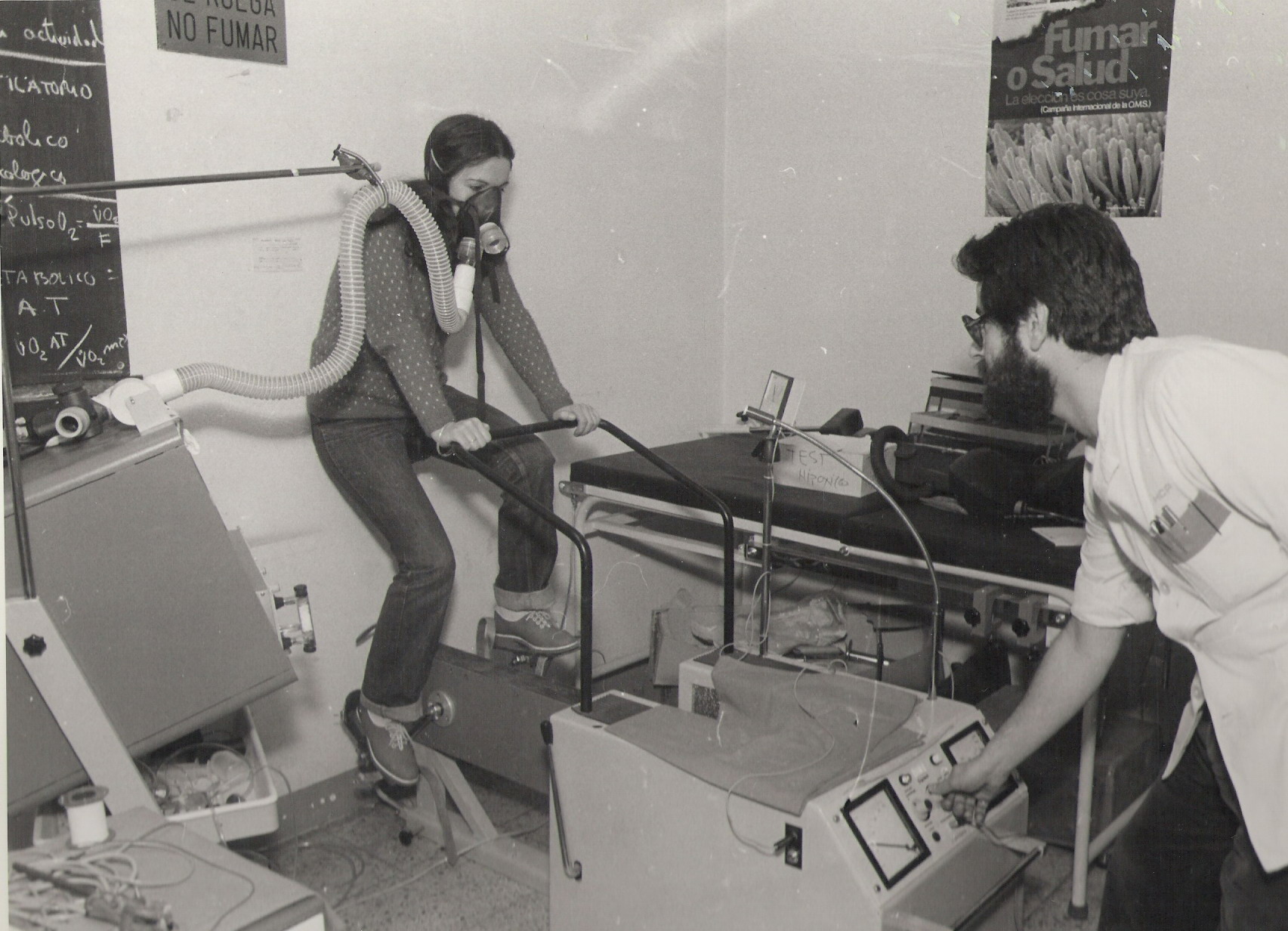
Exercise testing, 1978, Jaeger. Jaeger Exercise bike with mixing chamber. Photo courtesy of Felip Burgos, MSC, RPFT, RN. Barcelona, Spain.
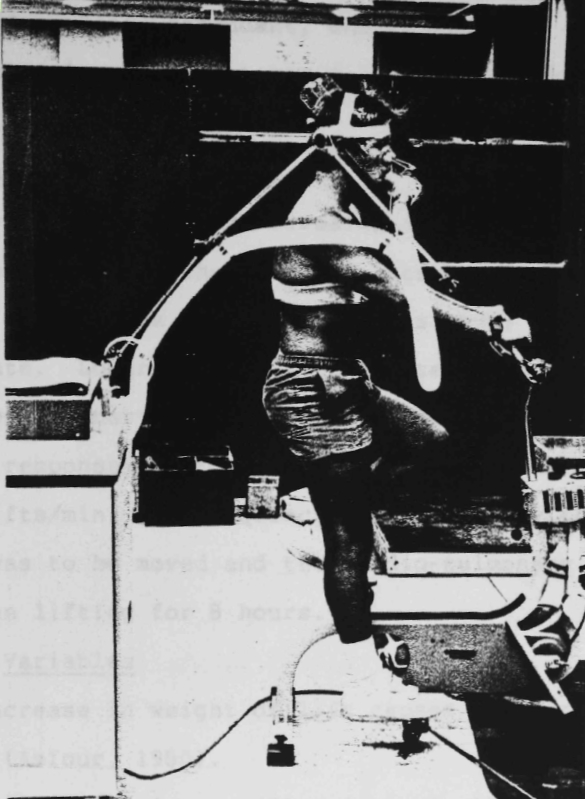
Exercise testing, 1986, Beckman Metabolic Cart. From a doctoral thesis on the Maximal Acceptable Weight of Lift by J.E. Fernandes