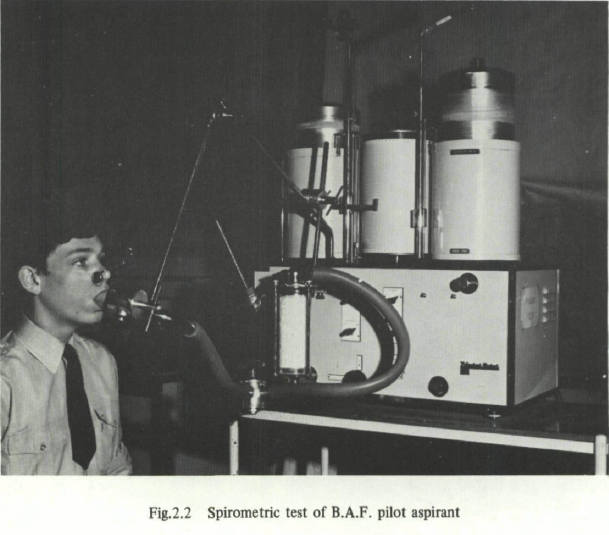
From: Survey of Current Cardiovascular and Respiratory Examination Methods in Medical Selection and Control of Aircrew by A. Scano, NATO Agardograph No. 196, published December 1974, page 46.
Monthly Archives: June 2014
Godart Pulmotest, 1974, Spirometry
Godart Pulmotest, 1974
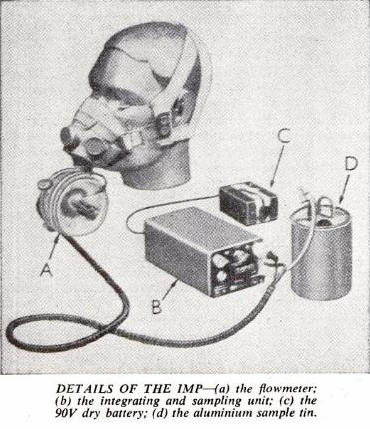
Integrating Motor Pneumotachograph (IMP), 1956
Integrating Motor Pneumotachograph, 1958
From New Scientist, November 29, 1956, page 21.
“…it will be necessary to measure their bodily energy exchanges; and this can be done with a modern apparatus called the IMP (integrating motor pneumotachograph). This consists of a light air pump and flowmeter housed in a plastic box, which connects on one side with a mask fitted over the face and on the other with a sample-collecting unit packed in a bag worn on the back. The IMP measures, over a given time, the total volume of air breathed out by its wearer, and from this expired air it automatically takes representative (or integrated) samples. The whole apparatus is so light, well-fitted and comfortable that it can be worn easily during violent exercise or peaceful sleep.
“The IMP was designed by Mr. H.S. Wolff, of the Human Physiology Division of the National Institute for Medical Research, to enable physiologists to study human energy exchanges under conditions ranging from swimming the Channel to bathing a baby. It has attachments allowing the wearer to drink through a tube or blow a whistle; though as yet the IMP cannot measure man’s energry exchanges while he is chatting, smoking, shaving or eating. It is manufactured by J. Langham Thompson.”
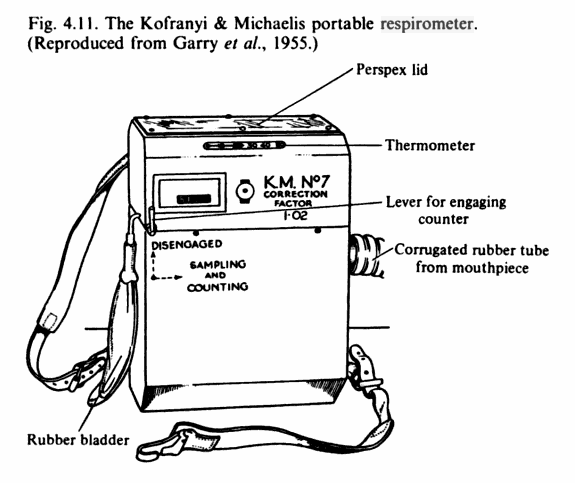
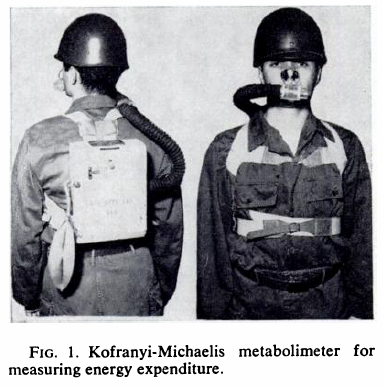
Metabolimeter, Kofranyi-Michaelis, 1955
Metabolimeter, Kofranyi-Michaelis, 1971
From Consalazio CF, Energy expenditure studies in military populations using Kofranyi-Michaelis respirometers, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, December 1971, page 1432.
“This simplified and compact unit is fairly small, 20 by 27 by 11 cm, weighs 3 kg, and consists of a dry gas meter for measuring the total volume and temperature of expired air. The aliquoting device can eb set to continuously remove 0.3 or 0.6% of each breath of expired air into a 500-ml butyl rubber bag. One important feature is that these aliquots can be taken over fairly long periods of time. These aliquots are analyzed for their CO2 and O2 concentration by conventional procedures and the eventual calculation of energy expenditure.”