I was reading James Hansen’s textbook on pulmonary function testing (one of my more interesting reads lately) and in passing he mentioned using the VA/TLC ratio as a way to measure ventilation inhomogeneity. The VA/TLC ratio has also been called the Va,eff/VA ratio and the VA’/VA ratio by different researchers but regardless of what it is called it is the ratio between a single-breath TLC measurement (VA) taken from a DLCO test and a multi-breath (helium dilution or N2 washout) or plethysmographic TLC.
A single-breath TLC regardless of whether helium, nitrogen, methane or argon is used tends to underestimate TLC even in individuals with normal lungs (and if the ratio > 1.0 then there is likely a technical problem with either the lung volume or DLCO measurements). This is mostly because of the limited time a single breath of tracer gas has to mix and diffuse evenly throughout the lungs. The idea is that a low VA/TLC ratio indicates poor gas mixing and therefore an elevated ventilation inhomogeneity.
The VA/TLC ratio is a relatively simple approach towards measuring ventilation inhomogeneity largely because the results can be derived from regular TLC and DLCO measurements. It was first proposed as a measurement over 40 years ago but despite having several notable proponents it has not achieved any particular level of acceptance.
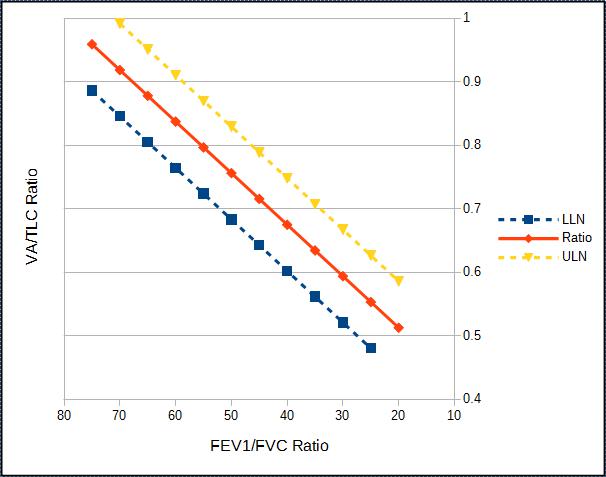
Part of the reason for this may be that there is limited agreement about what a constitutes a normal VA/TLC ratio. Cotes et al suggest that the ratio decreases slightly with age and stated that the normal range is 0.9 to 1.0 at age 20 and 0.85 to 0.95 at age 60. Roberts et al, however, in a study with a reasonably large population (n=379) selected for the presence or absence of certain conditions (normal, asthma, COPD) found no particular correlation with age (or height, weight and gender) and stated that in individuals with normal FEV1/FVC ratios the LLN was 0.828. Punjabi et al in a retrospective study of 5369 individuals unselected except for the presence of acceptable test quality stated that for FEV1/FVC ratios above 0.70 the VA/TLC ratio was 0.98.
There is general agreement however, that the strongest correlation between TLC and VA is an individual’s FEV1/FVC ratio.