Described in the August 11, 1882 issue of Medical News. “New spirometer: M.G. Bellange has recently constructed an apparatus for the measurement of the capacity of the chest, the amount of air expired in a given time, and the amount of exhaled gases. It consists of a mouthpiece, a spirometer and a carbonimeter.” Taken from: http://www.webimed.net/Spiro_1889.html
Monthly Archives: March 2014
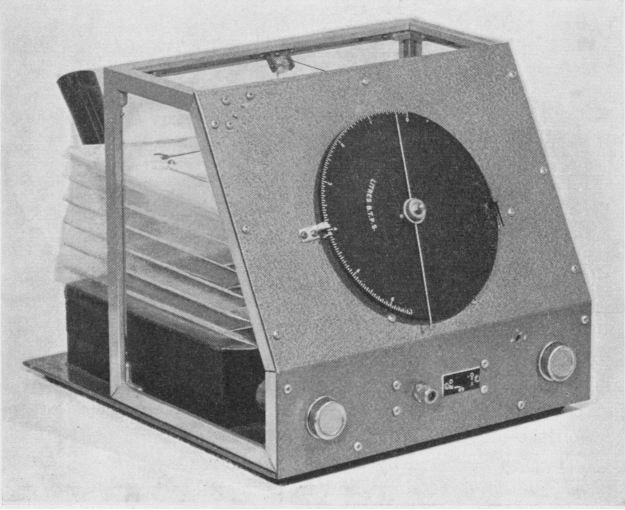
National Cylinder Gas Pulmonary Function Indicator, circa 1970’s
National Cylinder Gas Pulmonary Function Indicator, probably manufactured in the 1970’s. Used a hot-wire transducer to measure flow. Taken from an Ebay listing.
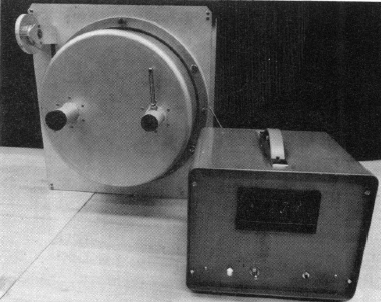
Spirometer, CPI Model 200, 1974
CardioPulmonary Instruments (CPI) Model 200. Horizontal rolling seal spirometer. Shown with a EPA-designed timer.
From: Burton RM, Kozel WM, Penley RP, Ward GH, Chapman RS. Application and evaluation of portable field instruments for measuring Forced Expiratory Volume of children and adults in environmental health surveys. Environmental Health Perspectives, 1974; 8: 123-131. Page 126.
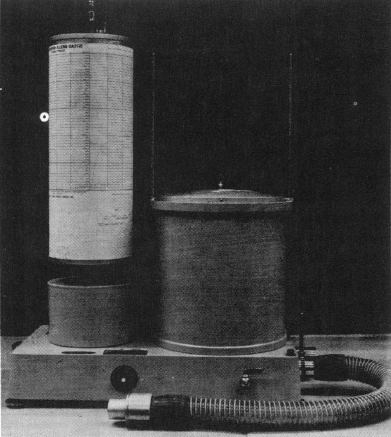
Spirometer, National Cylinder Gas Pulmonary Function Indicator, 1974
National Cylinder Gas (division of Chemtron) Pulmonary Function Indicator, 1974. Used a hot-wire transducer to measure gas flow.
From: Burton RM, Kozel WM, Penley RP, Ward GH, Chapman RS. Application and evaluation of portable field instruments for measuring Forced Expiratory Volume of children and adults in environmental health surveys. Environmental Health Perspectives, 1974; 8: 123-131. Page 125.
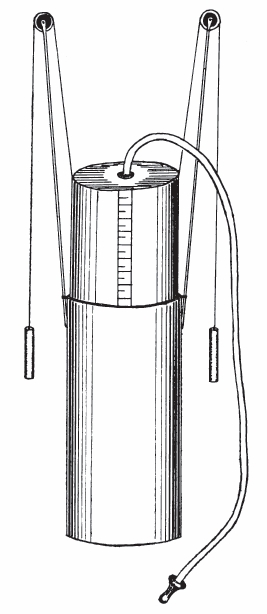
Spirometer, Collins Stead-Wells, 1968
Collins Stead-Wells Spirometer, circa 1968.
From: Burton RM, Kozel WM, Penley RP, Ward GH, Chapman RS. Application and evaluation of portable field instruments for measuring Forced Expiratory Volume of children and adults in environmental health surveys. Environmental Health Perspectives, 1974; 8: 123-131. Page 124.
Spirometer, Spalding’s, 1901
From: A manual for physical measurements for use in normal schools: public and preparatory schools, boys’ clubs, girls’ clubs, and young men’s Christian associations, with anthropometric tables for each height of each age and sex from five to twenty years, and vitality coefficients, by William Walter Hastings, Phd. Published by the International Young Men’s Christian Association Training School, 1901. page 18.
“The pupil, after loosening the clothing about the chest and taking a full inspiration, filling the lungs completely, should blow steadily into the spirometer until all the air possible has been expelled from the lungs. Two or three trials may be allowed.”
Recording U-Tube Mercury Manometer
A recording mercury U-tube manometer. The float in the left side of the U-tube moves up and down in response to respiratory pressures. The thin metal rod attached to the float had a recording pen at its tip.
From Das Stottern. Eine Monographie für Aerzte, Pädagogen und Behörden by Hermann Gutzmann, published by Rosenheim, 1898. page 149.
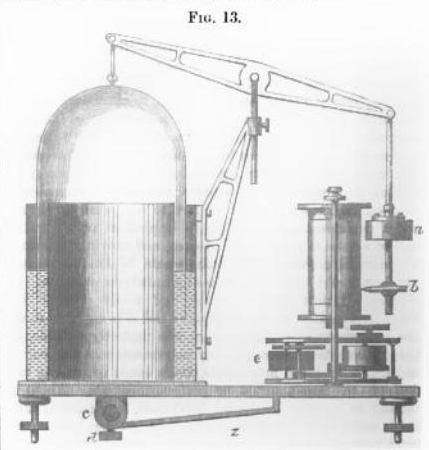
Spirometer, Modified Hutchinson, 1898
Purported to be a Hutchinson spirometer in the text of the article, this looks a lot more like a conglomeration of several different designs instead. The manufacturer was not named but was likely German.
From Das Stottern. Eine Monographie für Aerzte, Pädagogen und Behörden by Hermann Gutzmann, published by Rosenheim, 1898. page 148.